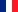
ALS is a devastating neurodegenerative disease characterized by the selective and gradual degeneration of motoneurons in the brain and spinal cord. A persistent inflammatory response contributes to ALS pathogenesis. Reactive astrocytes and blood-derived/resident immune cells play a pivotal role by governing the extent of the inflammatory response which can encompass both neuroprotective and deleterious functions.
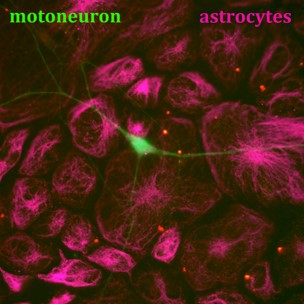
Our main goal is to identify death signals emerging from reactive astrocytes, immune cells and evaluate their potential as therapeutic candidates and determine their human relevance.
We already identified Fas (CD95), IFNg, LIGHT and TWEAK as determinants of non-cell-autonomous mediators of neuroinflammation and selective extrinsic death factors.
Nos techniques
- Cultures primaires de cellules neurales et non-neurales
- Motoneurones dérivés de cellules ES
- Chambes microfluidic
- Thérapie génique et immunotherapie
- Histopathologie
- Jonctions neuromusculaires
- Comportement moteur
Major publications
Coque E. et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 116, 2312-2317, 2019
Bowerman M. et al., Hum Mol Genet, 24, 3440-3456, 2015
Otsmane B. et al., EMBO Rep 15, 540-547, 2014
Aebischer J. et al.,Cell Death Diff. 18: 754-68, 2011
Mastroeni R. et al., Ann Neurol. 66: 177-22, 2009
Raoul C. et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103: 6007-12, 2006
Raoul C. et al., Nat Med. 11: 423-28, 2005
Raoul C. et al., Neuron. 14:411-3, 2002
Collaborations
- Patrick Aebischer et Bernard Schneider (EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland)
- Javier Hernandez (Montpellier, France)
- José Boucraut (Marseille, France)
- David Devos, Lille, France
- Luc Dupuis, Strasbourg, France
- Pascal Leblanc, Lyon, France
- Delphine Bohl, Paris, France
- Pierre-François Pradat
- Peter Bede
- Hélène Blasco
- Naomi Taylor and Valérie Zimmermann
Funding sources
ARSLA
AFM
ANR
E-RARE
Target ALS
Radala Foundation